European Filing Rules
From XBRLWiki
(diff) ←Older revision | Current revision | Newer revision→ (diff)
CEN Workshop Agreement
Status: Working Group Working Draft
CEN WS XBRL Experts: Thierry Declerck (DFKI), Roland Hommes (Rhocon), Katrin Heinze (Deutsche Bundesbank)
Editing rules
Editorial comments should be highlighted as follows: A comment
Text or rules in discussion (white): Some text
Text or rules already aligned (green): Some text
Text or rules to be deleted (red): Some text
Text to be delivered (blue): Some text
Contents |
Foreword
Some text
Introduction
The eXtensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) specification provides a high degree of flexibility in the creation of XBRL instance documents. Part of this flexibility stems from the nature of the syntax: XML, and part stems from the XBRL specification itself. This document is providing a guidance for regulators, on the syntax used in XBRL instances, to enable them to make restrictions where they feel they are appropriate.
Disclaimer:
The filing rules represent a collection of recommendations to be seen as an advice to be implemented in the European supervisory reporting process. The rules are also recommended to be adopted by national supervisors for other reporting purposes when they do not contradict their needs, i.e. footnotes are sometimes necessary to explain the content of reported fact. The listed filing rules are influenced by the European Taxonomy Architecture in cases where the instance creation is affected.
This document is listing best practices for the benefit of clear guidance on preparation and validation of XBRL instance documents and an increase of interoperability between computer applications that process these instances. Consistent use of the best practices facilitates the analysis and comparison of XBRL instance documents for both reporting entities as well as receivers in the reporting process. One goal of this document is to minimize the reporting burden for reporting entities in Europe. This goal is however subjective to reporting legislation as implemented by National and European regulators.
Notwhitstanding the only authoritative restrictions are respectivelly the XBRL specifications and the regulatory instructions, the following set of rules helps to avoid unnecesary complications by adopting well stablished best practices.
The grammar used to express some of the best practices is tightly connected to the the environment these practices were developed. I.e. guidelines stemming from Global Filing Manual or Edgar Filing Manual are based on RFC 2119. On the other hand the CEN projects are using the grammar from CEN T/C 123.
The guidance in this document is in the form of notes that will not make any strong texts on rules being a must/shall or should/recommended because it is not this document that has a mandate to put down rules. Only National and European regulators may have such a mandate. They can choose from the guidelines presented here to create their own set of rules.
Objective
The primary objective of the CWA1 working group is interoperability, by harmonization and guidance in the XBRL taxonomy creation process as carried out by regulators, supervisory authorities, voluntary supply chains and others.
The secondary objective is to facilitate adoption, by maintaining technological requirements when creating XBRL instance documents and keep them as simple as possible.
The fundamental use case that guides the following guidelines is the submission, by a reporting entity, of its regulatory filings, and the consumption of those regulatory filings by (several) reporting applications.
The following texts provides guidance on the preparation and validation of instance documents in XBRL format.
The guidelines in this document also aim to facilitate the analysis and comparison of reporting data as well as the interoperability of computer applications.
Target Audience
This document is intended for a technical audience and assumes that the reader has a working knowledge of the XBRL 2.1 and the XBRL Dimensions 1.0 Specifications and has a basic understanding of XML, Namespaces, and XML Schema.
To readers with XML knowledge, many of the guidelines in this document will be familiar however, others originate from features that are XBRL-specific and therefore the reasoning behind them may be less obvious.
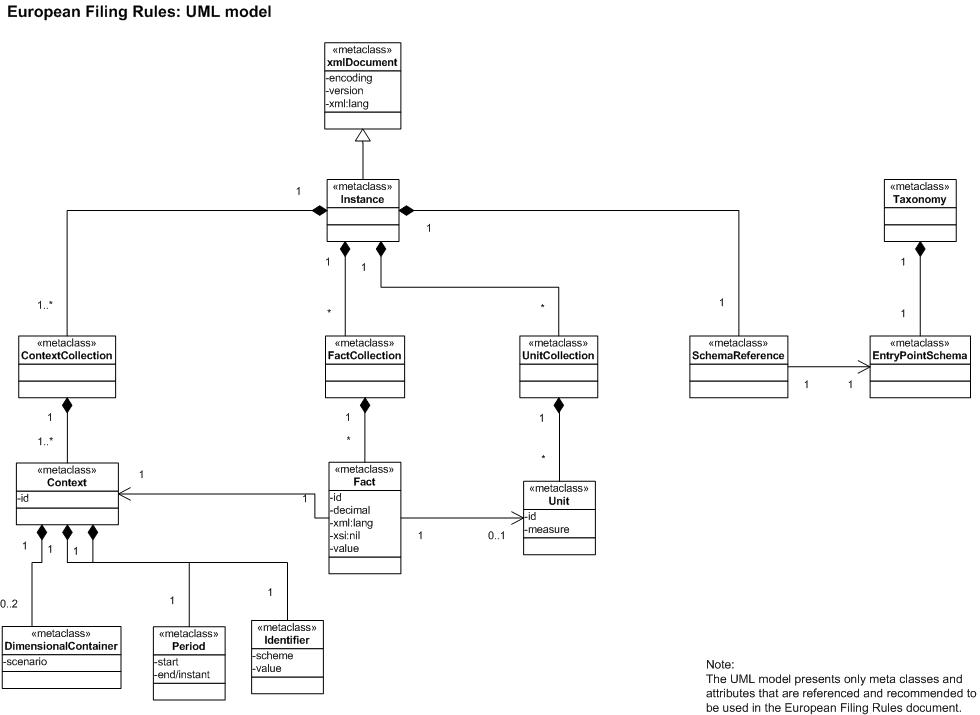
To ease the understanding by software developers implementing these guidelines in their reporting system, an UML model has been created to show the relationships between the different XBRL objects mentioned in this document.
Relationship to Other Work
The guidelines in this document pertain to XBRL filings. Parts of this document reiterate for expository clarity certain syntactic and semantic restrictions imposed by XBRL, but this document does not modify XBRL. In the event of any conflicts between this document and XBRL, XBRL prevails. This document does place additional restrictions beyond those prescribed by XBRL.
Scope
The guidelines in this document have been created for regulatory filings in the context of European supervisory reporting. In this document, “regulatory filings” encompasses European reporting standards that are published by an European supervisory authority and accompanied by an XBRL taxonomy as well as extensions on these taxonomies provided by national supervisors.
Normative references
Terms and definitions
- Applicable taxonomy
- An XBRL taxonomy recognised to use as a base for filings in a given filing system.
- Data point
- A data point is an information component that is defined by a supervisory authority to be sent in an instance document. In XBRL a data point is represented by a fact, its value and related dimensional combinations.
- Dimension
- A dimension is an xs:element in the substitutionGroup of xbrldt:dimensionItem; it relates to the ability to express multidimensional information;
- Entrypoint
- A schema or linkbase in the applicable taxonomy that represents the filing requirements and gets mentioned in the instance by the reporter.
- Fact
- A fact is an occurrence in an instance document of an element with a mandatory contextRef attribute and optional attributes like unitRef, xml:lang or xsi:nil.
- Filer
- A reporting entity.
- Filing
- A filing is the fundamental unit of information that is transmitted to a filing system for receipt, validation and acceptance. It is the conveyance of an XBRL instance document or series of XBRL instance documents.
- Filing system
- A system in which XBRL instance documents are filed, received, analysed and redistributed.
- Footnote
- A footnote is used to associate text annotations with particular facts in an XBRL instance document.
- Instance document
- An instance document is an XBRL file carrying facts. An instance document originating with a filer can only be sent as part of a filing. A filing comprises of one or more instance documents.
- Linkbase
- A linkbase is an XML file according to the XBRL 2.1 specification, containing relationships between concepts, resources and concepts and resources providing labels and references. There are different kinds of linkbases. One of them is the formula linkbase containing business rules in the syntax as prescribed by the XBRL Formula Specification.
- Publisher of the schema
- Organisation responsible for publishing a given XBRL taxonomy.
- Reporting entity
- A reporting entity is a institution or company with an obligation to prepare supervisory reports for national or European supervisory authorities.
- Taxonomy
- In the XBRL context, an electronic dictionary of business reporting elements relevant for reporting business data. A taxonomy is composed of an XML Schema and one or more linkbases directly referenced by that schema. ; Taxonomy creator : see Publisher of the schema
- XBRL specific terms like context, unit, period, entity, s-equal, v-equal see XBRL 2.1
Symbols and abbreviations
- UML
- Unified Modelling Language
- W3C
- World Wide Web Consortium
- XBRL
- eXtensible Business Reporting Language
- XML
- eXtensible Markup Language
Rules
Filing syntax rules
- 1.01
Filing naming
Common practice is to use the extension .xbrl for instance documents, but there is no technical restriction to use anything else. There are no restrictions on filenames posed. Different naming conventions exist around the world, essentially these are conveying some kind of meaning about: the sender, the reported filing and/or the reported period. For software that is storing the file name of the instance in a relational database some restrictions on which characters may be used and the total length of the file name may be appropriate.
CWA Advice: Rules about the file name of an instance document need to be set by the receiver of the reports, if required. - 1.02
Taxonomy selection
The reporter needs to be made aware on which taxonomy the instance should be creat-ed. This information is defined by the element link:schemaRef which carries the URL to the respective taxonomy. A listing of all taxonomy files respective modules recog-nised in the filing system should be provided by the publisher of the schema.
CWA Advice: Reporting entities are required to use one of the taxonomies as specified in the filing system as the applicable taxonomy. [FRIS04] - 1.03
Character encoding of XBRL instance documents
An XBRL instance document contains characters. Depending on the region in the world a multitude of characters could be interpreted as the (local) standard. If no rules are set arabic, kanji, cyrillic and latin could all be used in a single document.
CWA Advice: "UTF-8" is the recommended required encoding for XBRL instance documents. [GFM11, p. 11]
context xmlDocument inv:
self.encoding = 'UTF-8'
A published taxonomy can be discovered through entrypoints, which are defined by the taxonomy author. If multiple entrypoints are available in a single taxonomy the taxonomy author needs to provide clarification to the reporter, which entrypoint is to be used for which report. If multiple reports are allowed to be reported within a single instance problems may arise upon processing because the reported facts in the instance do not point to the entrypoint used. Data point modelled taxonomies may contain mul-tiple tables but these are not treated as an entrypoint. Only the whole of the taxonomy has a single entrypoint for all tables. Through the 'FilingIndicators' it is communicated which tables are communicated in the instance.
CWA Advice: Reporting entities are required to use only one entrypoint schema, as specified in the applicable taxonomy, per XBRL instance. [SBR13, p. 6]
Each XBRL instance in the filing is tested separately for XBRL 2.1 and XDT 1.0 va-lidity. In order to increase the likelihood that instance documents pass validation, filers are encouraged to validate their compliance with the XBRL 2.1 and Dimensional 1.0 specification prior to submission.
CWA Advice: Instance documents are required to be XBRL 2.1 and XBRL Dimensions 1.0 valid. [EFM11, p. 6-8]
context Instance::isXBRLValid() : Boolean
post: result = true
Any formula linkbase discovered by the XBRL software from opening the entrypoint can contain tests on the quality of the reported data. The tests that report an error on these data SHOULD be corrected. There MAY be tests that produce only warnings. Solving these warnings depends on the message content and the filer perspective on them.
XML-XBRL: If the XBRL Formula linkbase is discovered by the XBRL enabled software, and it has the capacity to execute assertions as defined in the XBRL Formula specification, these will result in true/false statements. Whether this points to an error situation in the instance is determined by the formula author, who may clarify the situation found in a message. There are no rules preventing processing of XBRL instances that contain formulae errors.
CWA Advice: It is recommended to have the XBRL instance document valid with regards to XBRL Formula as defined in the applicable taxonomy.
context Instance::isFormulaValid() : Boolean
post: result = true
XBRL Taxonomies can be extended by anybody with the proper technical knowledge. Filings to European Regulatory Authorities are 'closed form' i.e. all data points allowed by the regulator are in the taxonomy. There can be no extension of the taxonomy by reporters to report more data points to the regulator. However national supervisors may extend European taxonomies. For reporters the combination of base and extension taxonomies are regarded as a single taxonomy.
CWA Advice: Reports are required to contain only concepts created by the taxonomy author.
context Taxonomy inv:
self.owner = ‚European Banking Authority’
or self.owner = ‚European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority’
In case corrections are needed on filings that already have been sent, it is recommend-ed not to send partial data with just the corrected facts. Non-complete submissions could lead to invalid instance documents (according to either XBRL 2.1, XDT 1.0 or appropriate Formulae) and might raise conflicts with already processed data in the re-porting system of the receiver.
CWA Advice: It is recommended that reporters always send the full applicable dataset for an applicable entrypoint schema in an instance document, unless the receiver indicates otherwise.
Instance syntax rules
- 2.01
@xml:base
XML processors interpret this attribute differently, and there is no semantic need for this attribute.
XML-XBRL: The attribute xml:base may be inserted in XML documents to specify a base URI other than the base URI of the document or external entity.
CWA Advice: It is recommended that the attribute @xml:base not appear in any instance document [EFM13, p. 6-7]
context xmlDocument inv: self.element->select(xml:base)->isEmpty()
The version of any report is represented in folder names, not in URI namespaces. To correctly interpret the reported facts the proper entrypoint schema and its taxonomy must be present in the instance by including the full path (including the folder with the version indicator in it) in the link:schemaRef node.
CWA Advice: It is required to have the link:schemaRef contain the full URL as published on the internet.
Although version 1.1 exists, the whole of the XBRL specification is based around XML version 1.0. Unexpected results with XML enabled software can occur if the in-stance is based on XML version 1.1, even if no actual XML constructs from this ver-sion are used in the instance document.
CWA Advice: It is required to use @xmlversion=1.0.
context xmlDocument inv: self.version = '1.0'
Declaring unused namespaces is uncalled for and clutters the instance document.
CWA Advice: It is recommended to actually use namespace prefixes once they have been declared in the instance document [FRIS04].
Most schema authors provide a namespace prefix for their targetNamespace. It is common practice to re-use these prefixes in other XML documents when needed. It may lead to confusion to human readers to see common understood prefixes used on a different namespace. Eg. the prefix 'xs' for the http://xbrl.org/2003/xbrl-instance-2033-12-31 namespace.
CWA Advice: It is recommended that declaredto use the same namespace prefixes mirror the namespace prefixes as defined by their schema author(s) [FRIS04].
The element link:schemaRef can occurs several times in an instance. Nevertheless taxonomy authors will make sure that only a single entrypoint schema needs to be referred to in the instance. This entrypoint will refer all required data points. (See also 1.04)
CWA Advice: It is required to have only one xbrli:xbrl/link:schemaRef node in any XBRL instance document.
context Instance inv: self.SchemaReference->size() = 1
Entrypoints will be defined by means of a schema, and considering footnote linkbases are not supported, there is no use for link:linkbaseRef.
CWA Advice: It is required to refer to the taxonomy from the instance only by means of the link:schemaRef node.
Comments inside the instance that do not get reported as a fact will be ig-nored by the receiver. These comments clutter the instance and have no use to the regulator. Some instance creator tools include the software identification as an XML comment.
CWA Advice: It is recommended that an instance contains only contexts, units, schemaRefs and facts.
Context related rules
- 2.10
Duplicates of xbrli:xbrl/xbrli:context
Duplication is formed if all children nodes and values of the xbrli:context node with the exception of the @id on the context itself, are the same.C ontexts are defined to be equivalent if they have S-equal identifiers, equal dateUnion values for startDate, endDate and instant (respectively), and segment or scenario ele-ment children with equal QNames for each explicit and/or typed dimension. Duplicat-ed contexts are not prohibited by XML processors but they do not express extra se-mantics and potentially disturb comparison of facts that point to any of the duplicated occurrences [EFM13, p. 6-8].
CWA Advice: It is recommended to avoid having duplicates of xbrli:xbrl/xbrli:context nodes [FRIS04].
context Context inv: self.allInstances()->forAll(c1, c2| c1 <> c2 implies (c1.DimensionalContainer.scenario <> c2.DimensionalContainer.scenario and c1.Identifier.value <> c2.Identifier.value and c1.Identifier.scheme <> c2.Identifier.scheme and(c1.Period.start <> c2.Period.start and c1.Period.end <> c2.Period.end or c1.Period.instant <> c2.Period.instant)
The id attribute is meant as unique technical key within a XML document. Conveying semantics in the id attribute will go lost when the XML content is stored in a database (which generally work with database specific subrogated keys). Even though there is no limitation on the length of an id attribute it is recommended to keep it as short as possible.
CWA Advice: It is recommended to refrain from expressing semantics in the xbrli:context/@id node.
Unused contexts (contexts which are not referred to by facts) clutter the instance and add no value to either regulator or reporter [GFM11, p. 12].
CWA Advice: It is required to prevent unused xbrli:context nodes to be present in the instance [FRIS04].
context Context inv: self.Fact.allInstances()->notEmpty()
The @scheme contains a meaningful string to the regulator receiving the instance. This string represents an URI which refers to a list of issued keys to all reporters.
CWA Advice: It is required to use a code or pattern corresponding with the scheme that is prescribed by the national or European regulator that is receiving the XBRL instance [GFM11, p. 11].
Example: <xbrli:identifier scheme="http://www.kredittilsynet.no">NO12345678</xbrli:identifier>
let schemeUrl : String = ‘http://www.kredittilsynet.no’ -- URL to be replaced context Context inv: self.Identifier.allInstances()->forAll(scheme = schemeURL)
The XBRL specification allows for any content in the xbrli:identifier node.
CWA Advice: It is required to use a number or identifier recognoisedrecognized in the filing system of the regulator [GFM11, p. 11].
There can only be one reporter of an instance. Even if the content of the instance deals with a group of companies, there is only one entity reporting the instance to the regulator.
CWA Advice: It is required to have all xbrli:identifier content to be identical [EFM13, p. 6-8].
context Context inv: self.Identifier.allInstances()->forAll(i1, i2| i1 = i2 implies i1.value = i2.value)
see explanation on 2.15
CWA Advice: It is required to have all xbrli:identifier/@scheme content to be identical.
context Context inv: self.Identifier.allInstances()->forAll(i1, i2| i1 = i2 implies i1.scheme = i2.scheme)
European regulators will allow only dates to represent the reporting period by the XML Schema type xs:date.
CWA Advice: It is required to have all the xbrli:period date elements expressing ccyy-mm-dd format only [GFM11, p. 16].
The extreme version of duration is 'forever'. The XBRL specification has created this to solve problems with dates starting 'at the beginning' and ending 'never'. E.g. the name of the filer has in general no end date. The regulator is only interested in type of data for the reported time segment that has a defined starting and ending date.
CWA Advice: It is required not allowing xbrli:forever as a valid reporting period [GFM11, p. 19].
context Context inv: self.Period.forever->isEmpty()
When the values in xbrli:startDate and xbrli:endDate in the same or consecutive con-texts are equal, it may be unclear what the exact reporting period is. If however con-secutive 24 hour reporting periods are allowed by the regulator, explicit guidelines on interpreting the context reporting periods must be provided.
XML-XBRL: The XBRL specification has a semantic interpretation that a date used as a context/startDate as midnight at the beginning of that day. A context/instant or context/endDate means midnight at the end of that day.
CWA Advice: It is recommended not allowing equal xbrli:startDate and xbrli:endDate values [EFM13, p. 6-9].
context Context inv: self.Period->select(start < end)->notEmpty()
CWA Advice: In an instance document reporting a fiscal year, non-numeric facts containing text about any portion of that or a prior year shall have an @contextRef to an xbrli:context for the reporting period year.
Example: in a fiscal year 2009 report a company describes litigation settled in fiscal year 2007. Nevertheless, the disclosure text should be in a context for fiscal 2009. A reporting period begins at 00:00:00 of its first day and ends at 24:00:00 of its last day, which is the XBRL 2.1 default for periods. Only the date, not the time part of the ISO 8601 date-times, should be used in contexts.
CWA Advice: In an instance document reporting a fiscal year-to-date, the non-numeric facts containing text about any portion of the year-to-date or prior year shall have an @contextRef to an xbrli:context representing the year-to-date.
Example: a company completes an acquisition in its second fiscal quarter. In its 3rd quarter fiscal report, the Acquisitions note contains text describing that same acquisition. The 3rd quarter text should be in the context for the first nine months (that is, the year-to-date).
The dates defined in xbrli:instant or xbrli:startDate / xbrli:endDate should not exceed the first or the last day of the reporting period in a single instance as required by the regulator.
CWA Advice: It is recommended that the periods defined in the contexts refer to the same reporting period.
Example: corrections on previous periods MAY be using a different (version of the) taxonomy to prevent possible conflicts with the receiving regulator</span>
context Context inv: self.Period.allInstances()->forAll(p1, p2| p1 = p2 implies (p1.start = p2.start and p1.end = p2.end) or p1.instant = p2.instant)
The taxonomy author will assign either the xbrli:segment or xbrli:scenario container node to the dimensional validation. The XBRL specification allows however for any other content that is schema valid to be put in these containers by the reporter.For consistency reasons and simplification of processing, European taxonomy authors use the xbrli:scenario node only.
CWA Advice: It is recommended to be using only a single container node (preference for xbrli:scenario) in the xbrli:context.
context Context inv: self.DimensionalContainer.segment->isEmpty()
The xbrli:scenario or xbrli:segment element MUST NOT be used for anything other than for explicit or typed members. Custom reporter XML schema content may create problems with the regulatory system.
XML-XBRL: The XBRL specification allows xs:any content. This means that all XML schema content can be stored (not just XBRL Dimensions).
CWA Advice: If an xbrli:scenario (or xbrli:segment) element appears in a xbrli:context, then its required for its children to be one or more xbrldi:explicitMember and/or xbrldi:typedMember elements, and not allowing any reporter custom content [EFM13, p. 6-8].
Fact related rules
- 2.25
Duplicate facts
An instance document must not have more than one fact having S-Equal element names, equal contextRef attributes, and if they are present V-Equal, unitRef attributes and xml:lang attributes, respectively. The values of the id attribute and the text content of the element are not relevant to detection of duplicate facts. Other rules forbidding equivalent xbrli:context and xbrli:unit elements ensure that duplicate values of the contextRef and unitRef attributes can be detected without dereferencing. The predicate V-Equal is as defined in the XBRL 2.1 specification. The V-Equal test is sensitive to the underlying data type, so the decimals attribute of ‘-6’ is V-Equal to decimals ‘-06.0’. In unusual cases the same fact may be presented with different levels of detail, such as “123456 Shares with decimals equal to ‘INF’”, and “120000 Shares with decimals equal to ‘-3’”. Instead of including both facts in the instance, the instance should contain only the more precise one [EFM13, p. 6-10].
XML-XBRL: Duplicate facts are XML-XBRL syntax valid. However, the semantic meaning may be unclear.
CWA Advice: It is required to prohibit two facts having the same element name, equal contextRef attributes and, if they are present, equal unitRef and xml:lang attributes, respectively [FRIS04], [EFM13, p. 6-10]. - 2.26
@precision
The meaning of the @precision can be expressed in @decimals, by stipulating a nega-tive value in the latter. This makes it possible to have two attributes expressing the same semantic information on a fact.
CWA Advice: It is required to be using @decimals as the only means for expressing precision on a fact [EFM13, p. 6-12]. - 2.27
@decimals
The @decimals is about the accuracy of the fact value. A positive value in @decimals mean the number of accurate digits to the right of the decimal point. A negative value in @decimals mean the number of non-accurate digits to the left of the decimal point. A value of INF in @decimals mean than all the digits are accurate. The XBRL proces-sors use interval arithmetic for validation. To enable XBRL Formulae calculations to be performed on instance values for validation purposes, no truncations or rounding or any other kind of change should apply to the numeric facts in the instance. See the ex-planatory RFC at http://www.xbrl.org/RFC/PDU/PWD-2008-10-09/PDU-RFC-PWD-2008-10-09.html.
CWA Advice: The accuracy of a numeric fact is required to be expressed using @decimals, with no truncation, rounding or any change in the original fact value. If the @decimals attribute of a numeric fact is not equal to “INF”, then the numeric fact is interpreted as interval arithmetic of the numeric fact ± ½(10@decimals). This rule is valuable when XBRL Formulas are used to validate the numeric facts. Example: The table below illustrates correct and incorrect use:Fact text @decimals value Interval range Left interval Right interval 2345.45 INF [-0 , +0] 2,345.45 2,345.45 2345.45 2 (-0.005 , +0.005) 2,345.445 2,345.455 2345.45 0 (-0.5 , +0.5) 2,344.95 2,345,95 2345.45 -2 (-50 , +50) 2,295.45 2,395,45 2345.45 -3 (-500 , +500) 1.845,45 2.845,45 2345.45 -6 (-500000 , +500000) -497,654,55 502345,45 - 2.28
@decimals accuracy
The decimals attribute is not a scale factor. The decimals attribute is not a formatting code; it does not indicate that the digits in the instance must subsequently be presented to a user in any particular way.
CWA Advice: It is required to have the @decimals value correspond to the accuracy of the corresponding amount as reported in the regulatory filing.
The @decimals attribute influences how numbers are interpreted in XBRL and any value for the @decimals attribute other than the value 'INF' implies interval arithmetic. Use the following table to select the correct value of the @decimals attribute for a fact so that it corresponds to the value as presented in instance documents.Accuracy of the amount Value of decimals attribute Exact monetary, percentage, basis point or any other amount INF Accurate to billions -9 Accurate to millions -6 Accurate to thousands -3 Accurate to units 0 Accurate to cents 2 Accurate to a whole percentage (i.e. basic points) 4
Examples: The table below illustrates correct use.Fact Value Value of decimals attribute A percentage of (exactly) 46% .46 INF An (accurate) profit margin of 9.3% .093 3 An (accurate) amount “in thousands” 100000 -3 An (accurate) amount “in hundreds” 100200 -2 [EFM13, p. 6-28], [GFM11, p. 45f.]
- 2.29
@xsi:nil
There is a difference in reporting facts with the value zero, empty or xsi:nil='true'. It is up to the regulator to determine the meaning of the different situations.
CWA Advice: It is required to use the @xsi:nil="true" if the concept is to be reported but cannot hold the value zero or any reportable value [EFM13, p. 6-23].
Data related to white cells could be reported with the according value, as zero or as unknown. The table below shows the different possible solutions:zero value The value of the fact is "0". <p-cm-ca:CapitalRequirements decimal="0" unitRef="EUR" contextRef="ctx_1">0</p-cm-ca:CapitalRequirements> nil value The value of the fact is not known or can't be received. <p-cm-ca:CapitalRequirements xsi:nil="true" unitRef="EUR" contextRef="ctx_1"></p-cm-ca:CapitalRequirements> not applicable information The value is inapplicable. The fact doesn't appear in the instance. - 2.30
decimal representation
The value of numeric facts must be expressed in the specified units, optionally with decimals, but with any change of scale. The content of a numeric fact should therefore not include any scale factors like “%”, The monetary are expressed in units, not in thousands or millions.
CWA Advice: It is required to have numeric facts expressed in units (optionally with decimals) as well as to be accurate to the @decimal value.
Examples:
The legal decimal representation (Backus-Naur Form) in XBRL is:
<digit> ::= "0"|"1"|"2"|"3"|"4"|"5"|"6"|"7"|"8"|"9"|"0"
<number> ::= ["+"|"-"]<digit>{<digit>}["."{<digit>}]
Examples: 0 +0. 1234 -1234 1234.56 +123456.7890123456
The value “twenty thousand” may appear in a numeric fact as any legal decimal representation of 20,000, such as
20000, 20000.0, or 020000. It must not appear as “20”.
The value “20%” may appear in a numeric fact as any legal decimal representation of .2, such as 0.2, 0.20,
000.2000.
The value “20%” must not appear in a numeric fact as “20”, “20/100”, “20%” or any variation of the integer “20”.
The language used on string based facts needs to be identified. This can be done by declaring the @xml:lang on the xbrli:xbrl element just once, or on every string based fact individually. No rules have been set for regulators allowing multiple language reportings (choices are to support all languages in a single instance or to require mul-tiple, language based, instances). The preferred option is to have multiple languages in a single instance.
CWA Advice: It is required to have clear policy to define the language for non numeric facts.
The @id on individual facts is meant to uniquely reference the fact from other XML constructs. E.g. a footnote.
CWA Advice: It is recommended not to use any @id on facts.
Unit related rules
- 2.33
Duplicates of xbrli:xbrl/xbrli:unit
Units are equivalent if they have equivalent measures or equivalent numerator and de-nominator. Measures are equivalent if their contents are equivalent QNames. Numera-tors and Denominators are equivalent if they have a set of equivalent measures. Dupli-cated units do not express extra semantics and potentially disturb comparison of facts that point to any of the duplicated occurrences [EFM13, p. 6-10].
CWA Advice: It is required not having duplicate units in an XBRL instance.
context Unit inv: self.allInstances()->forAll(u1, u2| u1 <> u2 implies (u1.id <> u2.id and u1.measure->asOrderedSet() <> u2.measure->asOrderedSet())
CWA Advice: It is required to prevent unused xbrli:unit nodes to be present in the instance [FRIS04].
context Unit inv: self.Fact.allInstances()->notEmpty()
XII has released a standard numeric data type registry: it has a schema with numeric type declarations, and each numeric data type is associated with consistent unit decla-ration measures, numerators and denominators. Use of this registry that contains all the usual units eases implementation in software and simplifies validation. Link: XII UTR
CWA Advice: It is recommended to have the xbrli:unit children referring the XBRL International Unit Type Registry (UTR) [EFM13, p. 6-17].
To express amounts in any currency, it is possible to use only xbrli:unit/xbrli:measure element whose content is the QName of (e.g.) iso4217:EUR [EFM13, p. 6-29]. But it is also possible to use xbrli:unit/xbrli:divide/xbrli:numerator with the iso4217 value and a xbrli:denoniator of '1000' or '1000000', which would introduce precision through the unit on a numeric fact. Precision is already covered by the @decimals on a fact. There should not be two methods of expressing the same.
CWA Advice: It is required to have units representing currencies, to represent the actual physical value of these currencies.
Amounts that a reported should refer to only to one xbrl:unit with a xbrli:measure that content is a QName starting with iso4217.
CWA Advice: It is required that an instance express its monetary values through the currency unit/s defined by the regulator.
context Instance inv: self.Unit->select(measure.substring(1, 7) = #iso4217)->size()=1
Footnote related rules
- 2.38
Footnotes
The tables of the European reporting frameworks consist of white, gray and criss-crossed cells. White cells can be reported if data is available and can be retrieved from the database of the reporting entity. Gray cells could be reported but they are not man-datory because the level of detail is excluded from the reporting. Crisscrossed cells make no sense from an economic point of view. Additional information to white cells outsourced in footnotes cannot be handled by regulators; all information is captured in datapoints that are reflected in concepts.
CWA Advice: It is required that information in the instance is included in the appropriate concepts only.
Bibliography
- [GFM11] Global Filing Manual (Interoperable Taxonomy Architecture Project)
- [EFM13] EDGAR Filer Manual U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission
- [FRIS04] IFRS Taxonomy Guide
- [SBR13] SBR FRIS rules 2013