DPM2MDM
From XBRLWiki
(diff) ←Older revision | Current revision | Newer revision→ (diff)
CEN Workshop Agreement
CEN WS XBRL Experts: Ignacio Santos (Bank of Spain), Roland Hommes (Rhocon), Katrin Heinze (Deutsche Bundesbank)
Contents |
Foreword
This document has been prepared by CEN/WS XBRL, the secretariat of which is held by NEN. CWA XBRL 001 consists of the following parts, under the general title Improving transparency in financial and business reporting — Harmonisation topics:
- Part 5: Mapping between DPM and MDM
Introduction
This document aims to provide an introduction in the topic of creating a conceptional model for storing multidimensional data which is received by XBRL instances that follow the rules defined by European taxonomies published by EBA (European Banking Authority) or by EIOPA (European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority).
Disclaimer: The multidimensional data model presented in this document is intended to be a starting point for a subsequent modelling process to be adapted to specific analytical or transactional needs. It solely refers to the concepts of DPM (Data Point Model) and EXTA (European XBRL Taxonomy Architecture) to be used in the European supervisory reporting.
The purpose of this document is to present and explain the mapping between the Data Point Model (DPM) and the Multidimensional Data Model (MDM) [1] [2] [3] [4] [5], through the Relational Model using ROLAP analytic tool. This document is based in a work presented in Banca D’Italia, Rome, in September 2011 [20]. ROLAP is defined as Relational Online Analytical Processing. The DPM is a semantic model (Logical Model). Experts in the supervision in Europe have created the DPM, and as they are not software Engineers, they have important difficulties, especially with the XBRL specification [6]. XBRL taxonomies are metadata that provide a formal description of the data requirements to be used as data format in this case in the European reporting process. This document intends also to supply a description for IT experts about the linkage between a DPM as source and a relational data base as target of a transformation process.
The objective of the European XBRL Taxonomy Architecture (EXTA), is to set a framework or set of architecture guidelines that enables a Discoverable Taxonomy Set (DTS) author to create an XBRL taxonomy. However in this document expect to help to design the taxonomy through the DPM and in turn, it can implement the DPM in a Database. But, moreover, to help to Information System (IS) to have a better comprehension of the metadata. Comment-01
This project is funded by the EU commission to support the standardization process for supervisory reporting in Europe.
Objective
The objective of the EXTA is to define a set of architecture guidelines that transform a European DPM without a loss in quality in a XBRL format. The taxonomy architecture provides a set of rules for this transformation to enable the creation of consistent and predicable XBRL meta definitions in an automated process. On the other hand CEN WS has built a guidelines for mapping the DPM in the MDM. In such a way that the architect of IS can understand and/or mapping the DPM to ROLAP.
Target Audience
EXTA is targeted at taxonomy authors. Initially organizations like European Banking Authority (EBA), European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA), European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA), European Central Bank (ECB) are the authors of these taxonomies. As a spin-off of these taxonomies, local (national) initiatives will emerge, hosted by National Supervisory Agencies (NSA’s). The audience of this document are financial or economic institutions, agencies, companies, or Universities that they want to implement the taxonomies in a relational model.
Relationship to other work
The reader of this EXTA is expected to be familiar with the principles of data modelling and have an understanding of the XBRL family of the specification. But, also, it is necessary to have a knowledge in the relational model and in the MDM.
Scope
The DPM has been defined for the creation of Data Point Models in the context of European supervisory reporting. Data Point Model by an European supervisory authority. To reflect the defined structures in a machine-readable from the can be accompanied by an XBRL taxonomy. It is also possible to extend the described methodology to other environments as Database. Comment-02
Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this document, the following terms and definitions apply. The terms definitions used in the mapping with Data Point Model are inspired by vocabulary already known through their use for describing multidimensional databases and data warehouses. IT specialists originally introduced these terms. However, for an understanding and creation of Data Point Models they are established in the language of business specialists as well.
In this section are shown the set of definitions necessaries for mapping the DPM in ROLAP. The majority of the definitions are obtained of [6] [7] [8] [9] [10]. When the definition is in the area of CEN WS XBRL (Main Page) [11] [22] only is shown a hyperlink to definition.
The terms used directly or indirectly in the mapping of DPM in the MDM are:
- Concept.
- Data Point Model.
- Dimension.
- Domain.
- Family.
- Framework.
- Item.
- (Domain) member.
- Metric.
- Namespace.
- Owner.
- Perspective.
- Public elements.
- TableGroup.
- DataPoint.
- DataCube.
- Module.
- Hypercube.
A hypercube is an abstract item declaration in the xbrldt:hypercubeItem substitution group. A Hypercube is an ordered list of dimensions, defined by the set of zero or more dimension declarations linked to the hypercube by hypercube-dimension relationships in a dimension relationship set, and ordered according to the order of this relationship [10].
In the DPM a hypercube is reflect in the DataCube. A DataCube is a set of DataPoints with its appropriate Dimensions and Members.
A hypercube in the MDM is a set of pairs <dimension, attributes of dimension> and calculated attributes defining one or more facts [19].
- Taxonomy.
- Context.
The context element contains information about the entity being described, the reporting period and the reporting scenario, all of which are necessary for understanding a business fact captured as an XBRL item [6].
In the MDM, the context is defined as a set of dimension of a fact or group of facts. A context belongs to an entity or financial institution, for a period, a meaning for the business (segment), and a scenario. The scenario shows the specific pairs of dimension and the dimension attribute of business logic [9].
Mapping from Data Point Model to Multidimensional Data Model
Introduction
This section presents the mapping between the DPM and the Relational model through ROLAP. In this mapping is not expected the transformation to XBRL taxonomies, however is possible its conversion [20]. Moreover, also, in this transformation is not established any process of validation. It is only mapped the DPM structure in the Relational model. However, it is expected that the reader of this document can understand better the DPM or even that the reader can store the DPM in a RDBMS (Relational Database Management System), using the MDM.
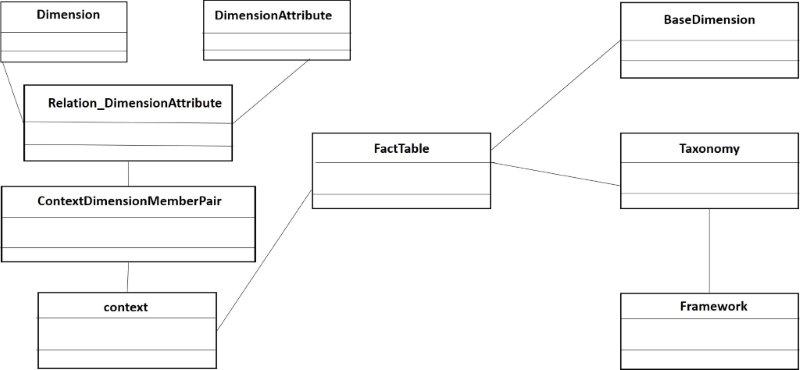
Like the aim of this document is to obtain a star model from the DPM. That is to say, the DPM is mapped to the MDM in Databases. The figure 1 shows the MDM of the DPM.
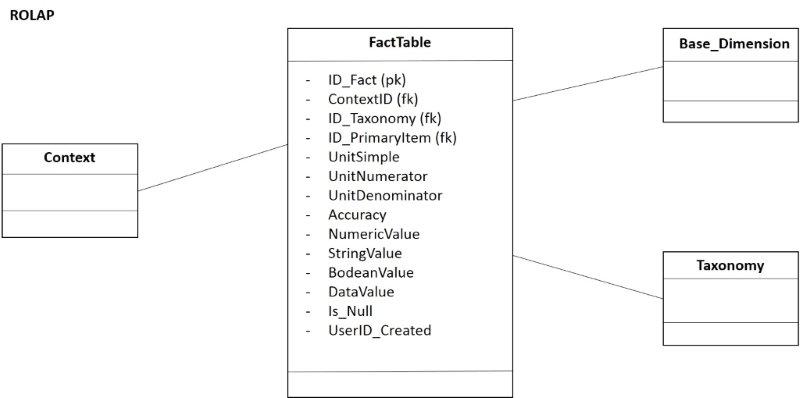
The object FactTable is the DataPoint, in the MDM is the fact table. It is a star model, because, to fact table goes in three dimensions, BaseDomain (set of primary items), Taxonomy and Context. To dimension Taxonomy goes in the dimension Framework. To the context goes into the dimension Context_Dimension_DimensionAttributes.To the last dimension the set of dimension/attributes of dimension. And, to the set dimension/attributes of dimensions the dimensions end DimensionAttributes. Also, it is possible to add the dimension familie to Dimensions, that it is not drawn, according to not complicate the drawing.
- Figure 1. Star model of the DPM using ROLAP tool.
In the annex B is shown its implementation in a RDBMS, moreover, it is also displayed the diagram of this implementation.
There are a lot of bibliography about the mapping from different sources to a relational database especially from XML [12] [13] [15] [21], and about query in heterogeneous sources is interesting the paper of Levi et al. [14]. Nevertheless, the process of transformation of this section is based in Taentzer et al. [15}. This section will go step to step with the different constructors that they are corresponding in the DPM.
In this section the process of conversion is analysed. Normally, in a first step is to study the DPM element or element to transform. After, the mapping between the DPM element and the Relational elements. The transformation process in the figures show the DPM UML graph on the left hand side to UML class diagram to display the Relational model (ROLAP) from MDM. The black arrows between both UML language but customized extensions which are used to describe the graph transformation. The square between two black arrows contains an abbreviation what is begin mapped. In this document are distinguished the next different types of mappings rules between the two graphs [15]:
- A2A is the automatic transformation between attributes to attributes.
- A2Pi is the automatic transformation between classes to the primary item.
- A2T is the automatic transformation between attributes to taxonomy.
- C2C is the automatic transformation between concepts.
- C2CTx is the automatic transformation between classes to contexts.
- C2CTxDM is the automatic transformation between classes to Contexts, dimensions, and attributes of dimension.
- C2D is the automatic transformation between classes of dimensions to dimensions.
- C2DA is the automatic transformation between classes to attributes of dimension.
- C2F is the automatic transformation between concepts and frameworks.
- C2Fact is the automatic transformation between classes and the fact table.
- C2Pi is the automatic transformation between classes to the primary item.
- C2T is the automatic transformation between concepts and taxonomy.
- T2T is the automatic transformation between taxonomies.
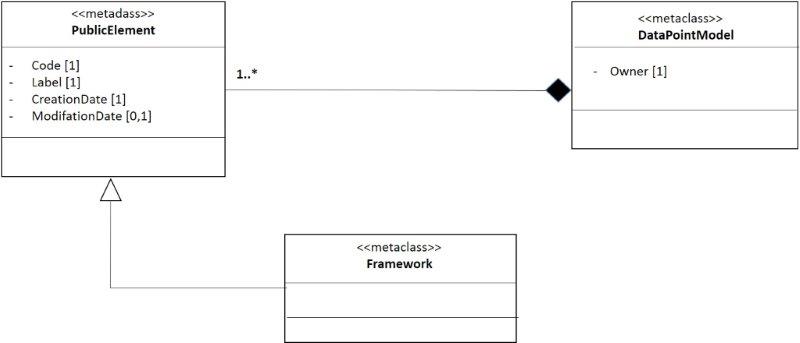
Framework
The figure 2 shows the perspective structural of the framework and this is an extract of the figure 1 in the DPM [22]. The Data Point Model has from 1 to N public elements. From a public element inherits different classes, as element of the dictionary or frameworks [11] [22].
- Figure 2. Structural perspective of the framework.
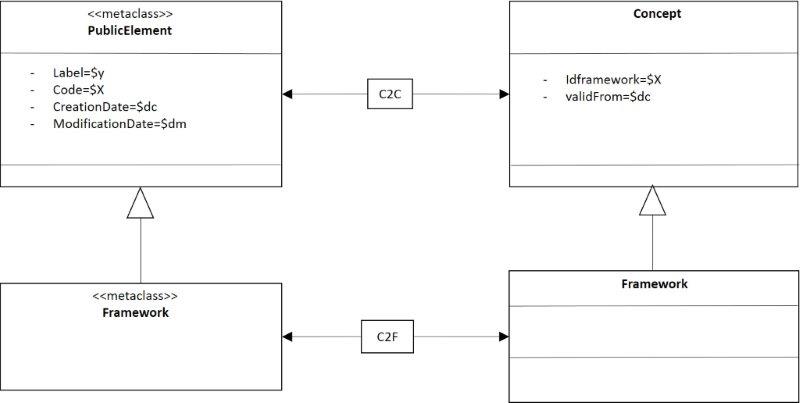
The figure 3 show the transformation of the class public element and framework. The aim is to obtain the constructor Framework. For this publicElement is mapped in a constructor concept and the framework in relational model, as the constructor. In figure 3 can be omitted the mapping of publicElement to concept, if the class framework has inherited the necessary element of publicElement. However, the figure 3 maintains it for comprehension. The constructors in figures in the Relational Model are classes (as in UML, the Stereotype by default is a class, in the figures are omitted the word class), and this is implemented in the relational model as tables.
- Figure 3 Mapping for the framework.
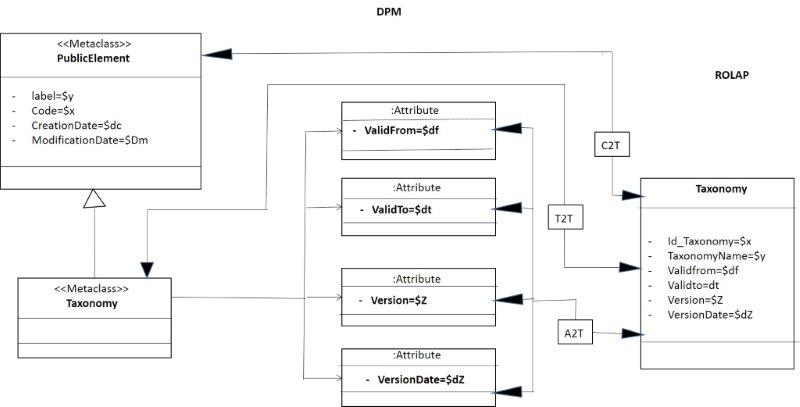
Taxonomy
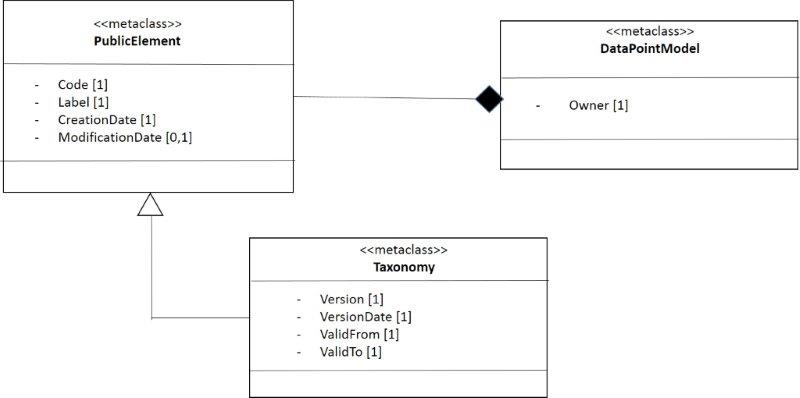
In the same way the class taxonomy inherits of public element [11] [22], as figure 4 shows.
- Figure 4. Structural perspective of the taxonomy.
In figure 5 is shown the mapping between the class Taxonomy of the DPM and the constructor Taxonomy and the RM (Relational Model). However, in this figure are add details as the breakdown of some attributes of the class taxonomy, for clarifying better to reader of this document.
- Figure 5. Mapping for the constructor taxonomy.
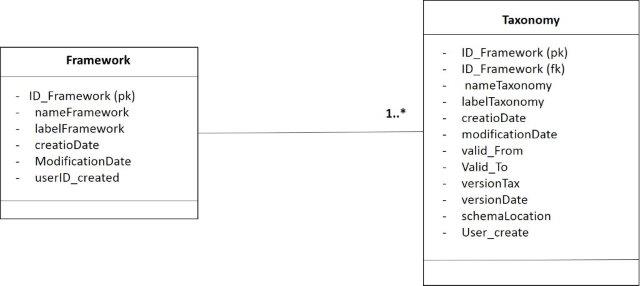
On the other hand, in the Relational Model (RM) a class framework has 1**n classes taxonomy.
- Figure 6. Ralationship between framework and taxonomy in the relational model.
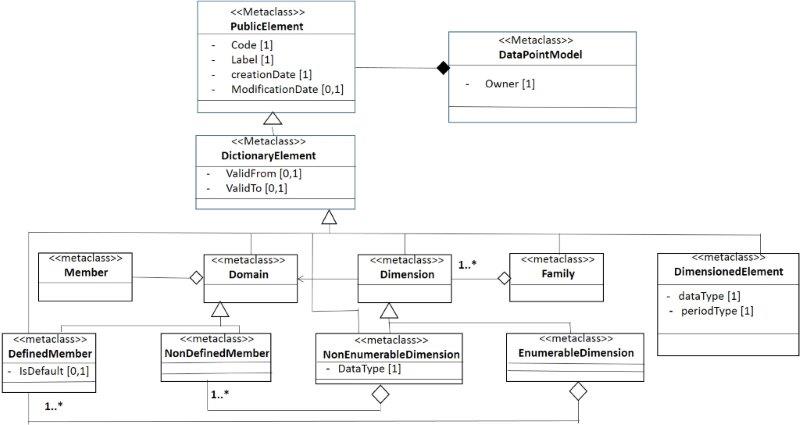
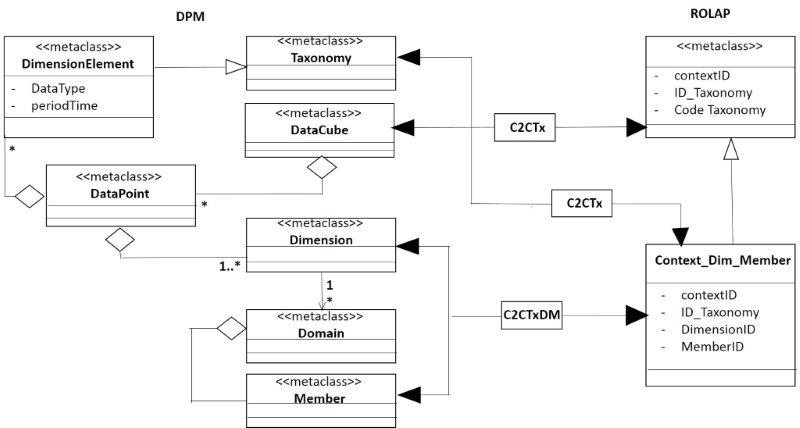
Dimensions
In this section is defined the mapping of the constructor dimension. The figure 7 shows a perspective of the structure of the dimension and this is an extract of the figure 1 in the DPM [22].
- Figure 7. Structural perspective of the dimension.
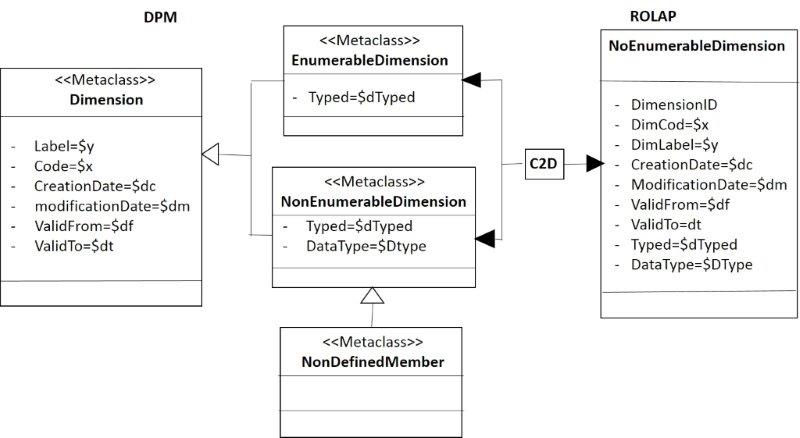
This figure shows two types of dimensions [9] [10], the enumerable and the non-enumerable dimensions. But in an upper level is the family or group of dimensions and they belong to a same domain, it is not mapped to MDM. On the other hand, a non-enumerable dimension is not known in advance, then in th RM is not shown until the document instance is obtained.
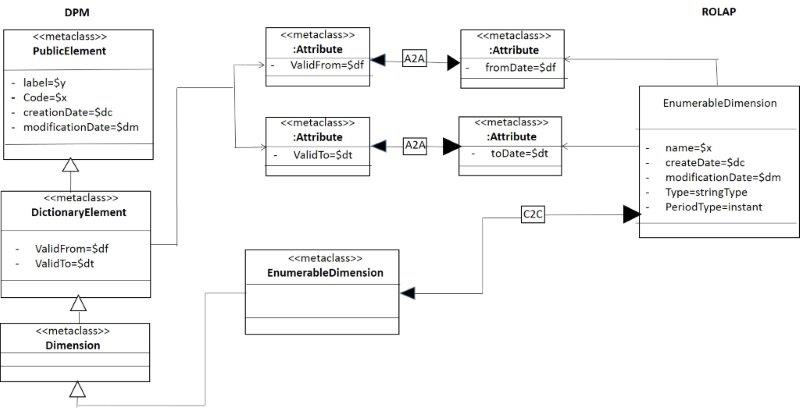
The figure 8 shows only the mapping of the enumerable dimension. Where the transformation between DictonaryElement (DPM) and EnumerableDimension (RM) is detailed a little more, for comprehension of the reader.
- Figure 8. Mapping for Enumerable dimensión.
The figure 9 depicts the transformation of the DPM to ROLAP, and the reverse mapping of the typed and explicit dimensions. In this figure is added the union between the non-enumerable or enumerable dimension.
- Figure 9. Mapping of transformations for dimensions.
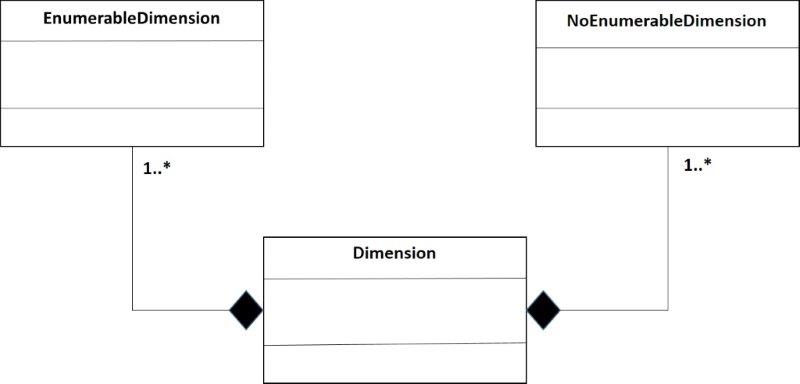
However, in the Relational model both constructors are one, enumerable and non-enumerable. The entity Dimension entity will have an attribute for showing if the dimension is non-enumerable or enumerable and another attribute with the data type, figure 10.
- Figure 10. RM, the constructor dimension.
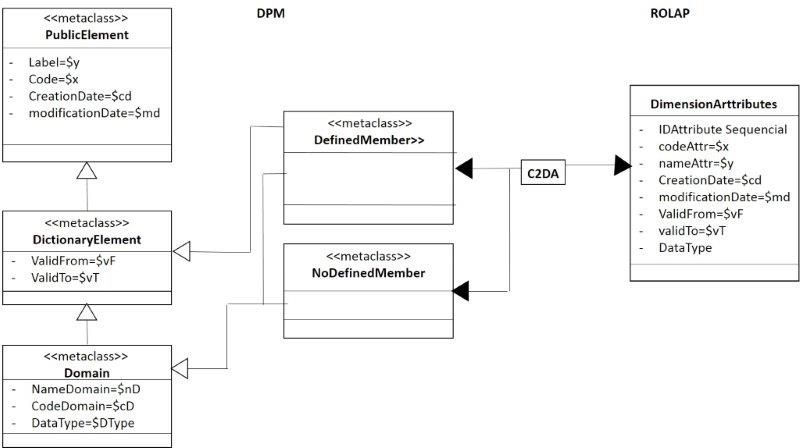
On the other hand, from the members defined or not are obtained the dimension attributes of the dimension, figure 11. But in both cases they will defined in this constructor, although they are filled out when the taxonomy is defined or in run time of the document instance. The figure 8 shows the mapping of the dimension attributes with the members.
- Figure 11. Mapping of members defined or not to dimension attributes.
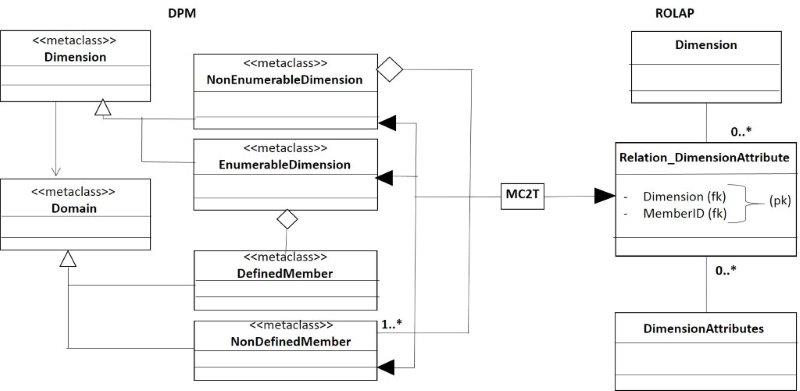
The figure 12 shows the mapping of Dimensions and domain-members in the DPM and Dimensions/Dimension attributes in the Relational data model (ROLAP).This figure really is an artifice, because is not necessary the mapping from the DPM.
- Figure 12. Mapping of the Relations.
Context
The context is not part of the DPM but of the XBRL instance structure. The corresponding UML model is included in the filing rules document of CWA1 [23].
The figure 13 shows the mapping of DPM to the Relational Model. There are two Context and another for the context with the dimensions and the domains-members. In the relational model the dimensions can be explicit or typed.
In the mapping is obtained two constructor for the RM, the Context_taxonomy, and Context_Dim_Member. A context in the DPM is a DataCubes with the same set of dimensions but in different taxonomies. This makes that this context has meaning different depending on the taxonomy. For this the context is shared by the taxonomy. Moreover, each context has a set of dimensions (explicit or typed) with its domain-member (if is explicit). Then, it is defined another constructor contex_Dim_Member. Each object of this constructor is a dimension/member/context.
- Figure 13. Mapping of the context.
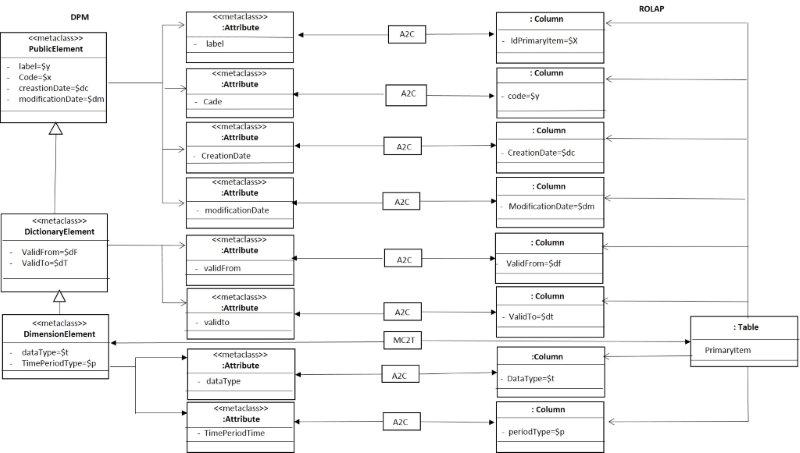
Primary Items
The primary item could be a domain-member of a dimension, however, is a little special, because is associated with this concept two attributes, the type of the data and the time period type. The figure 14 shows the mapping with the relational model. The set of primary items are grouped in the base dimension, in this figure is called the constructor PrimaryItem.
- Figure 14. Mapping for the Base Dimension (set of primary items).
Fact table or Data points
The fact table, figure 16, in the MDM (Data point in the DPM) is the union of the table context, set of primary items or base dimension and taxonomy.
- Figure 16. diagram ROLAP of the fact table of the DPM.
ANNEX A. Metamodel defined by the EBA (FINREP and COREP) mapped to MDM.
Introduction.
This annex maps the relational model of the DPM supplied by the EBA in the MDM, using ROLAP tool.
The EBA published on 15 March 2013, and after a modification on 27 March 2013 the updated version of the templates, instruction, validation rules, and data point model for implementing technical standards (ITS) on supervisory reporting (COREP and FINREP [16]. On the other hand, in that date EBA published the DPM Database 0.1.1 as Meta model structure used as the repository all the metadata defined in the DPM from which the XBRL taxonomies will be derived. This annex will map this structure of the EBA to the relational data model [18]. The database is built from this document and with the help of a paper under review [19]. For a better understanding the implementation is done in MS SQLServer, version 2012, Sp1. However its move to other RDBMS is easy, because SQL is a standard. In a first step is created the structure of the DPM in the RDBMS (Relational Data Base Management System), SQL Server. And the second step is to populate the DPM in database with the datamodel of the EBA (DPM Database 0.1.1) through a tool ETL (Extract, transformation, and load).
The EBA in this example don’t provide any XBRL Document Instance, then it is not possible to fill out the fact table with an example, but the structure of the DPM is complete. However, in this model is considered a difference with this datamodel propose, the base dimension is a normal explicit dimension, therefore the table base dimension is empty.
Creation of the structure and load the DPM of the EBA in a RDBMS.
In the annex B is shown the creation of the structure of the DPM in RDBMS using the MDM, hosted by CWA1.
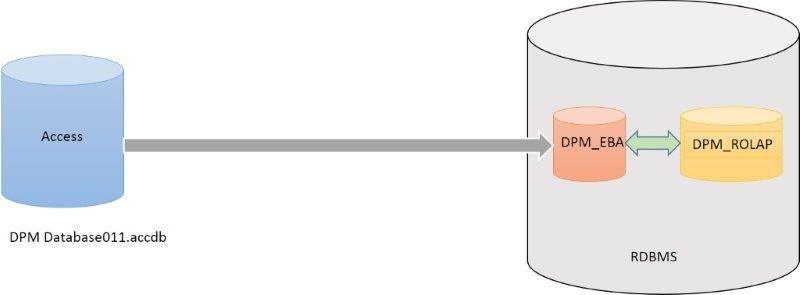
On the other hand, from the EBA webpage [16] is possible to download the zip file with the Metadata model structure, DPM Database 0.1.1. After the structure and data will be move to RDBMS. In this document is used MS SQL Server (there free edition). However, it is possible to use other RDBMs, as oracle, DB2, etc.. From Access to SQL Server in this document is used Integration Services IS of MS SQL Server (there is free edition). Through IS (Information Systems) is implemented the importation of the metadata. In this toll, the origin is the Access (The used driver is Microsoft Access (Microsoft Set Database Engine), and the target the client, SQL Server Native client 11.0 and the database, in this document the name is DPM_EBA. After, all tables have to be selected, and the packet is submitted. The figure 14 shows a general view of the load of the Access in a RDBMS and the mapping to DPM in a Relational Database.
- Figure 14. General view of Access and RDBMS of the EBA and the DPM in ROLAP.
Loading DPM_ROLAP from DPM_EBA.
This section makes a mapping from DPM_EBA to DPM_ROLAP, both database. The DPM_EBA is loaded in the above section. And DPM_ROLAP is created using the annex B of this document.
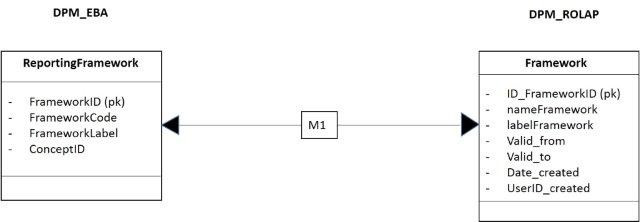
As first step, the table Framework_DPM is loaded from ReportingFramework. This load is shown in the figure 15, through its design and after the code. In the code of this document the dates are simulated.
- Figure 15. Mapping of the framework.
The code of M1 is:
use DPM_ROLAP
--
-- M1 CODE
--
--truncate table framework_DPM
delete from Framework_DPM
go
insert into Framework_DPM (ID_Framework, nameFramework, valid_from, userID_created)
select FrameworkID as ID_Framework,
FrameworkCode as nameFramework,
convert(datetime, '20130327', 112),
'EBA'
FROM DPM_EBA..ReportingFramework
go
select * from Framework_DPM
go
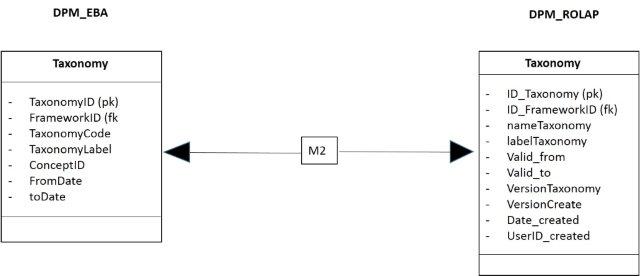
If the framework is loaded, next table is Taxonomy_DPM, that is loaded from the database DPM_EBA..Taxonomy. The figure 16 shows the mapping M2.
- Figure 16. Mapping of the taxonomy.
The code of the mapping M2 is:
use DPM_ROLAP -- -- code M2 -- --truncate table taxonomy_DPM delete from Taxonomy_DPM go insert into Taxonomy_DPM(ID_Taxonomy, ID_Framework, nameTaxonomy, labelTaxonomy, valid_from, versionTax, date_created, userid_created) select TaxonomyID as ID_Taxonomy, FrameworkID, TaxonomyCode, TaxonomyLabel, convert(datetime, '20130327', 112), '0', convert(datetime, '20130327', 112), 'EBA' from [DPM_EBA].[dbo].[Taxonomy] go select * from Taxonomy_DPM go
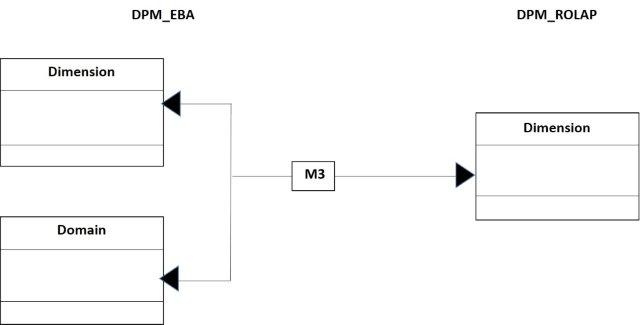
The next step is to obtain dimensions from the EBA, and it is shown in the figure 17.
- Figure 17. The mapping of dimensions.
The code of the mapping M3 is:
-- -- code M3 -- insert into Dimension_DPM (dimensionID, dimensionCode, dimensiondescr, domainID, typedDim, typeData, valid_from) select a.DimensionID, a.DimensionCode, a.DimensionLabel as dimensiondescr, a.DomainID, a.IsTyped as typedDim, cast(b.DataTypeID as nvarchar(30)) as typeData, convert(datetime, '20130327', 112) as valid_from from DPM_EBA.dbo.Dimension a inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.Domain b on a.DomainID=b.DomainID go select dimensionID, dimensionCode, dimensiondescr, domainID, typedDim, typeData, valid_from from dimension_DPM go
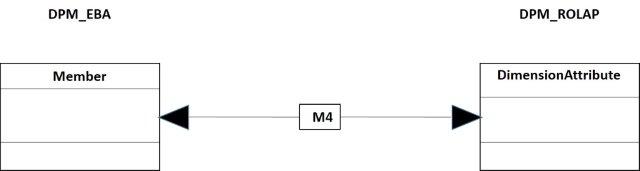
After, it is obtained the dimension attributes, as it is shown in the figure 18.
- Figure 18.- Mapping of the attributes of dimensión (ROLAP).
The code of the mapping M4 is:
--- --- Code M4 --- insert into Domain_Member_DPM(memberID, domainID, memberCode, memberDescr, byDefault, createFrom, valid_from) Select MemberID, DomainID, MemberCode, MemberLabel as memberDescr, IsDefaultMember as byDefault, convert(datetime, '20130327', 112) as createFrom, convert(datetime, '20130327', 112) as valid_from from DPM_EBA.dbo.Member go select memberID, domainID, memberCode, memberDescr, byDefault, createFrom, valid_from, valid_to from Domain_Member_DPM go
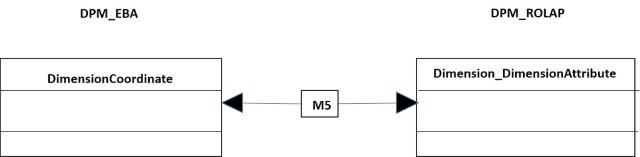
The relations between dimensions and attributes of dimension is shown in the figure 19.
- Figure 19. Relationship between dimensions and attributes of dimension.
The code of the mapping M5 is:
--- --- Code M5 --- insert into Dimension_Domain_Member_DPM( dimensionID, memberID) select DimensionID, MemberID from DPM_EBA.dbo.DimensionalCoordinate go select dimensionID, memberID from Dimension_Domain_Member_DPM go
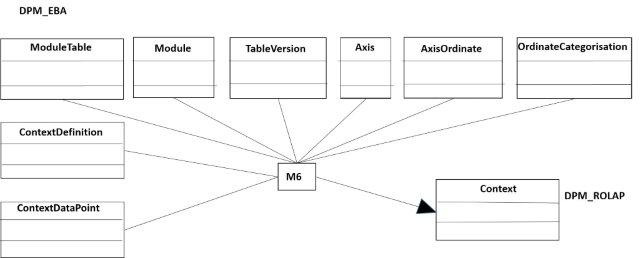
The next table is the context and the figure 20 shows the mapping. As a data point (a fact) can be referenced by a context, but this context belongs to a taxonomy, the context needs of the taxonomy (module is named by the EBA).
- Figure 20. Mapping of the context from DPM_EBA.
The code of the transformation M6:
--- --- Code M6 --- insert into context_DPM (contextID, ID_Taxonomy, contextDescr, codeTaxonomy) select g.ContextID, b.ModuleID as ID_Taxonomy, h.ContextKey as contextDescr, b.ModuleCode as codeTaxonomy from DPM_EBA.dbo.ModuleTable a inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.Module b on a.ModuleID=b.ModuleID inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.TableVersion c on a.TableVID=c.TableVID inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.Axis d on a.TableVID=d.TableVID inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.AxisOrdinate e on d.AxisID=e.AxisID inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.OrdinateCategorisation f on e.OrdinateID=f.OrdinateID inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.ContextDefinition g on (f.DimensionID=g.DimensionID and f.MemberID=g.MemberID) inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.ContextOfDataPoints h on g.ContextID=h.ContextID group by g.ContextID, b.ModuleID, b.ModuleCode, h.ContextKey go select contextID, ID_Taxonomy, contextDescr, codeTaxonomy from context_DPM go
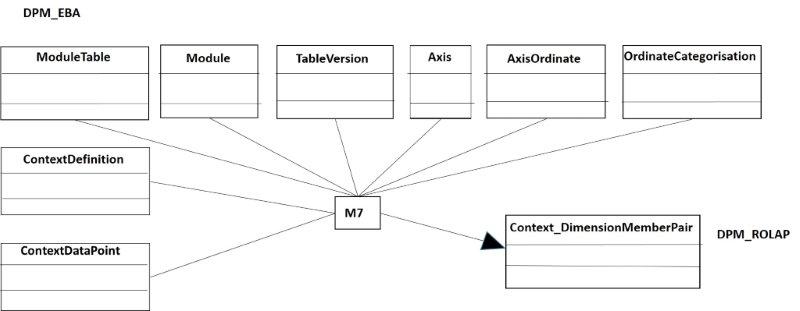
Regard the context and the dimensions and attributes of dimension the transformation can be analysed in the figure 21.
- Figure 21. Mapping of the Context_Dim_Members.
And the transformation code M7:
--- --- Code M7 --- insert into Context_Dim_Members_DPM(contextID, ID_Taxonomy, dimensionID, memberID) select g.ContextID, b.ModuleID as ID_Taxonomy, f.DimensionID, f.MemberID from DPM_EBA.dbo.ModuleTable a inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.Module b on a.ModuleID=b.ModuleID inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.TableVersion c on a.TableVID=c.TableVID inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.Axis d on a.TableVID=d.TableVID inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.AxisOrdinate e on d.AxisID=e.AxisID inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.OrdinateCategorisation f on e.OrdinateID=f.OrdinateID inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.ContextDefinition g on (f.DimensionID=g.DimensionID and f.MemberID=g.MemberID) inner join DPM_EBA.dbo.ContextOfDataPoints h on g.ContextID=h.ContextID group by g.ContextID, b.ModuleID, b.ModuleCode, f.DimensionID, f.MemberID order by b.ModuleCode, g.ContextID go select contextID, ID_Taxonomy, dimensionID, memberID from Context_Dim_Members_DPM go
ANNEX B. Implementation of the DPM in ROLAP.
Introduction.
This annex is divided in two sections, Relational model and the creation of the tables.
Structure ROLAP
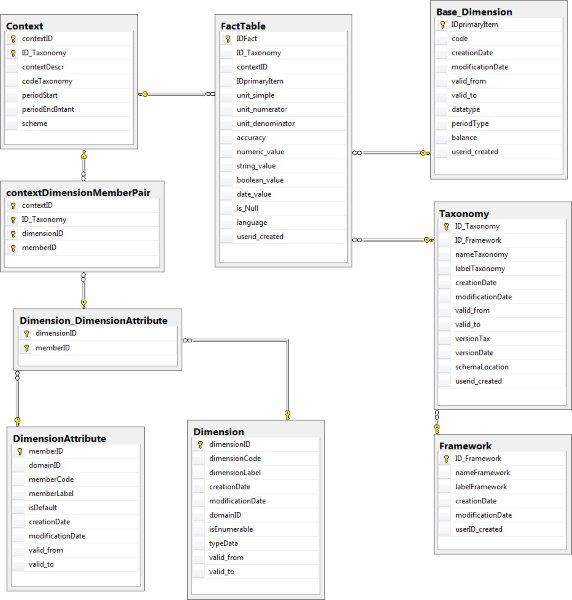
The figure 22 shows the relational model of the Data Point Model (DPM), through a relational diagram obtained from Management Studio of MS SQL Server.
- Figure 22.- Structure of the MDM of the DPM.
Creation of the infrastructure through MS SQL Server.
This Section shows the script of creation of the tables. The first part of this script delete the tables (all) and after the tables and some object more are created.
use DPM_ROLAP
go
IF OBJECT_ID(N'FactTable_DPM', N'U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE FactTable_DPM;
go
IF OBJECT_ID(N'Period_DPM', N'U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE Period_DPM;
go
IF OBJECT_ID(N'TR_Base_Domain_Balance_DPM', N'TR') IS NOT NULL
DROP TRIGGER TR_Base_Domain_Balance_DPM;
go
IF OBJECT_ID(N'Base_Domain_DPM', N'U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE Base_Domain_DPM;
go
IF OBJECT_ID(N'Context_Dim_Members_DPM', N'U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE Context_Dim_Members_DPM;
go
IF OBJECT_ID(N'Context_DPM', N'U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE Context_DPM;
go
IF OBJECT_ID(N'Dimension_Domain_Member_DPM', N'U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE Dimension_Domain_Member_DPM;
go
IF OBJECT_ID(N'Domain_Member_DPM', N'U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE Domain_Member_DPM;
go
IF OBJECT_ID(N'Dimension_DPM', N'U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE Dimension_DPM;
go
IF OBJECT_ID(N'Taxonomy_DPM', N'U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE Taxonomy_DPM;
go
IF OBJECT_ID(N'Framework_DPM', N'U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE Framework_DPM;
go
create table Framework_DPM (
ID_Framework int primary key,
nameFramework nvarchar(255) not null,
labelFramework nvarchar(255) null,
valid_from datetime not null,
valid_to datetime null,
date_created datetime not null default getdate(),
userID_created nvarchar(30) not null default current_user)
go
create table Taxonomy_DPM (
ID_Taxonomy int primary key,
ID_Framework int not null references Framework_DPM,
nameTaxonomy nvarchar(255) not null,
labelTaxonomy nvarchar(255) not null,
valid_from datetime not null,
valid_to datetime null,
versionTax nvarchar(10) not null,
versionCreated datetime not null default getdate(),
date_created datetime not null default getdate(),
userid_created nvarchar(30) not null default current_user)
go
create table Dimension_DPM (
dimensionID int not null primary key,
dimensionCode nvarchar(10) not null, --Code of approach dimension
dimensiondescr nvarchar(255) not null,
domainID int not null,
typedDim bit not null default(0), -- by default is explicit (0), if not typed (1).
typeData nvarchar(30) null,
ap_dim_nsuri nvarchar(200) null, --Namespace.
ap_dim_rem_code nvarchar(20) null, --Code of members.
pt_dim_code nvarchar(10) null, --Code of portfolio dimension.
pt_dim_nsuri nvarchar(200) null, --Namespace
pt_dim_mem_code nvarchar(20) null, --Code of members
ga_dim_code nvarchar(10) null, --Code of country dimension
ga_dim_nsuri nvarchar(200) null, --Namespace
ga_dim_rem_code nvarchar(20) null, --Code of members.
valid_from datetime not null,
valid_to datetime null
)
go
create table Domain_Member_DPM(
memberID int primary key,
domainID int not null,
memberCode nvarchar(50) not null,
memberDescr nvarchar(255) not null,
byDefault bit not null default(0), -- By default a domain-member is not the default
createFrom datetime not null,
valid_from datetime not null,
valid_to datetime null
);
go
create table Dimension_Domain_Member_DPM(
dimensionID int not null,
memberID int not null,
constraint PK_Dimension_Domain_Member_DPM
primary key (dimensionID, memberID),
constraint FK_dimensionID foreign key (dimensionID)
references Dimension_DPM,
constraint FK_memberID foreign key (memberID)
references Domain_Member_DPM
);
go
create table Context_DPM (
contextID int not null,
ID_Taxonomy int not null,
contextDescr nvarchar(255) not null,
codeTaxonomy nvarchar(255) null,
constraint PK_Context_DPM primary key (contextID, ID_Taxonomy)--,
--constraint FK_taxonomyID foreign key(ID_Taxonomy)
-- references Taxonomy_DPM
);
go
create table Context_Dim_Members_DPM(
contextID int not null,
ID_Taxonomy int not null,
dimensionID int not null,
memberID int not null,
constraint PK_Context_Dim_Members_DPM
primary key (contextID, ID_Taxonomy, dimensionID, memberID),
constraint FK_Context_Dim_Members_DPM_ContextID_ID_Taxonomy
foreign key (contextID, ID_Taxonomy)
references Context_DPM(contextID, ID_Taxonomy),
constraint FK_Context_Dim_Members_DPM_dimensionID
foreign key (dimensionID, memberID)
references Dimension_Domain_Member_DPM(dimensionID, memberID)
)
go
create table Base_Domain_DPM (
IDprimaryItem int identity(1,1) primary key,
code nvarchar(10) not null,
nsuri nvarchar(200) not null,
datatype nvarchar(20) not null
check (DataType in ('String','Monetary','Integer','Numeric')),
periodType nvarchar(10) not null
CHECK (PeriodType in ('Instant','Period','Forever')),
balance nchar(10) null
check (Balance in ('Credit','Debit')),
date_created datetime not null default getdate(),
userid_created nvarchar(30) not null default current_user
)
go
create trigger TR_Base_Domain_Balance_DPM ON Base_Domain_DPM
after insert, update
as
declare @Balance nchar(10),
@DataType nvarchar(20),
@code nvarchar(10)
select @code =code,
@Balance =balance,
@DataType =datatype
from inserted
if @Balance is null and @DataType='Monetary'
begin
raiserror ('If the DataType is Monetary the Balance attribute can not be NULL
ATTENTION: The PrimaryItem with name: %s is not inserted.', 16, 1, @code)
rollback transaction
end
go
go
create table Period_DPM(
IDPeriod int identity (1,1) primary key,
start_date datetime null,
end_date_Instant datetime not null,
instant_Year nvarchar(4) not null,
instant_month nvarchar(2) not null,
instant_day nvarchar(2) not null,
date_created datetime not null default getdate())
go
create table FactTable_DPM(
ID_DPM int primary key, -- Identification of the DPM or the Fact
contextID int not null,
ID_Taxonomy int not null,
IDprimaryItem int not null,
unit_simple nvarchar(10) null, --EUR, PURE, ETC.
unit_numerator nvarchar(10) null,
unit_denominator nvarchar(10) null,
accuracy dec(1) null, --Decimals value
numeric_value dec(17,4) null,
string_value nvarchar(4000) null,
boolean_value bit null,
date_value datetime null,
nil_value char(1) null, --CHECK: Y ODER N
date_crated datetime not null default getdate(),
userid_created nvarchar(30) not null default current_user,
CONSTRAINT CK_boolean_value_DPM CHECK (boolean_value in (1,0)),--CHECK: Y ODER N
CONSTRAINT CK_nil_value_DPM CHECK (nil_value in ('Y','N','y','n')),--CHECK: Y ODER N
constraint FK_FactTable_DPM_Context_Taxonomy
foreign Key (contextID, ID_Taxonomy)
references Context_DPM(contextID, ID_Taxonomy),
constraint FK_FactTable_DPM_Taxonomy
foreign Key (ID_Taxonomy)
references Taxonomy_DPM(ID_Taxonomy),
constraint FK_FactTable_DPM_primaryItem
foreign Key (IDprimaryItem)
references Base_Domain_DPM(IDprimaryItem)
)
Bibliography
- [1] Inmon W. H. (2005) Building the Data Warehouse, 4th Edition. John Wiley & Sons 2005.
- [2] Kimball R. (2004) The Data Warehouse Toolkit series. John Willey & Sons 1996-2004.
- [3] Jarke M., Lenzerini M., Vassiliou Y. and Vassiliadis P, (2003). Fundamentals of Data Warehouses, 2nd edition, Springer.
- [4] Kimball Group (2013). http://www.rkimball.com/html/articles.html.
- [5] Data Warehouse Institute (2013). http://www.tdwi.org”.
- [6] Engel P, Hamscher W., Shuetrim G., Vun Kannon D., Wallis H. (2008). Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) 2.1. July 2nd, 2008. XBRL International. http://www.xbrl.org/Specification.
- [7] Schmehl K (2009) Data Model and Matrix Schemas. November 16th, 2009. http://www.eurofiling.info . XI European Banking Supervisor, XBRL Workshop hosted by the Oesterreichische Nationalbank, Vienna.
- [8] Santos I, Castro E (2011) XBRL and the Multidimensional Data Model. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies, WEBIST 2011, pages 161-164, Noordwijkerhout. The Netherlands, May 6th-9th, 2011.
- [9] Santos I, Castro E (2011) XBRL Interoperability through a Multidimensional Data Model. IADIS International Conference on Internet Technologies & Society (ITS2011), Shanghai, China. December 8th-10th, 2011.
- [10] Hernandez-Ros I, Wallis H (2006) XBRL Dimensions 1.0 XBRL International. April 26th, 2006. http://www.xbrl.org/Specification/XDT-CR3-2006-04-26.rtf.
- [11] Declerck T, Homes R, Heinze K (2013) European XBRL Taxonomy Architecture V2.0. CEN Workshop Agreement. www.xbrlwiki.info/index.php?title=European_XBRL_Taxonomy_Architecture_V3.0.
- [12] Bernstein P A, Halevy A Y, Pottinger RA (2000). A vision for management of complex models, SIGMOD Record 29 (4), 2000, 55-63.
- [13] Chewathe S, García-Molina H, Hammer J, Ireland K, Papakonstantinou Y, Ullman J, and Widom J (1994) The TSIMMIS Project: Integration of heterogeneous information sources. In Proc. 10th Meeting of the Information Processing Societ of Japan, pages 7-18, 1994.
- [14] Levi A, Rajaraman A, and Ordille J (1996) Querying heterogeneous information sources using source descriptions. VLDB’96, Proceedings of Twenty-second International Conference on Very Large Data Bases.
- [15] Taentzer G, Ehrig K, Guerra E, Lara J, Lengyel L, Levendovszky T, Prange U, Varro D, and Varro-Gaypay S (2005) Model Transformation by Graph Transformation: A comparative Study. Model Transformation in Practice Workshop 2005 (MIIP2005).
- [16] EBA (2013) Update on the technical standards on supervisory reporting requirements. http://www.eba.europa.eu/-/update-on-the-technical-standards-on-supervisory-reporting-requirements.
- [17] Santos I (2013) Data Point Model (DPM) versus Multidimensional Data Model (MDM). Contribution for DPM chapter in CEN WS XBRL Plenary Session, Dublin, April 19th 2013. Hosted by Central Bank of Ireland.
- [18] Academy works (2013) Openfiling. http://www.oprmfiling.info?page_id=286.
- [19] Santos I, Castro E, Velasco M (2013) Conceptual and Logical Models in the Design of Economic and Financial Reports Using the XBRL Specification. In the journal Business & Information Systems Engineering (BISE), under review.
- [20] Santos I, Castro E (2011) Proof of concept of mapping a XBRL report versus a RDBMS. Openfiling 1st General Assembly, organized by XBRL Operational Network of the European Banking Authority, and hosted by Bank of Italy. September 5th, 2011. Banca d’Italia, Rome, Italy. http://www.openfiling.info/?page_id=286.
- [21] Della Penna G, Di Marco A, Intrigila B, Melatti I, and Pierantonio A (2003) Xere: Towards a Natural Interoperability between XML and ER Diagrams. Lecture Notes in computer Science, volume 2621 2003, pp 356-371. Book: Fundamental Approaches to software Engineering.
- [22] Declerk T, Hommes R, Heinze K (2013) European Data Point Methodology V2.0. CEN Workshop Agreement. European Data Point Methodology V2.0.
- [23] Declerk T, Hommes R, Heinze K (2013) European Filing Rules. CEN Workshop Agreement. European Filing Rules.