European Data Point Methodology
From XBRLWiki
(diff) ←Older revision | Current revision | Newer revision→ (diff)
This page will be soon filled with actual content. For now the reader can consult some documents published by EBA [1]
CEN Workshop Agreement
Status: Working Group Working Draft
Editing rules
Editorial comments should be highlighted as follows: A comment
Text or rules in discussion (white): Some text
Text or rules already aligned (green): Some text
Text or rules to be deleted (red): Some text
Text to be delivered (blue): Some text
Contents
|
Foreword
Some text
Introduction
The Data Point Methodology consists of a set of methodical procedures to create a multidimensional data point model that reflects detailed business aspects of supervisory frameworks. The result of the implementation of these procedures is a data point model which provides data structures represented in supervisory tables and underlying regulations that can be interpreted by IT applications. Data point models are created by banking specialists who are highly skilled in understanding supervisory reporting frameworks. This document defines technical requirements on data point models that need to be fullfilled when using data point models (1) for generating data formats for the reporting process or (2) for designing multidimensional database structures for the analysis of supervisory data.
The document intend to support the communication between supervisory experts and IT experts by introducing the concept of data point modelling and its underlying terms.
This guidance is in the form of notes in association with the pertaining requirements clause and uses the terms “MUST” (strong recommendation), “SHOULD” (recommendation) and “MAY” (possibility). Organizations wishing to implement this CWA (CEN Workshop Agreement) would be expected to consider all recommendations where the terms "MUST" and “SHOULD” are used.
Objective
A Data Point Modell consists of objects that reflect the supervisory data and its relations among each other that can be communicated and understood by computers. The objects of a data point model described in this document facilitate the ease of understanding of the data structure for technicians and reflects the rules to be met when using a data point model as basis for the generation of a data format or as basis for analysis purposes.
Target Audience
This document is being created to support Information Technology (IT) experts in the transfer of content from regulatory reporting to IT systems. It assumes that the reader has a working knowledge of the XBRL 2.1 and the XBRL Dimensions 1.0 Specifications as Data Point Models are being used as basis for generating XBRL taxonomies. Furthermore basic knowledge about Business Intelligence is assumed to understand the rules to be followed when designing multidimensional database structure for data warehouses.
Relationship to Other Work
Some text
Scope
The Data Point Methodology has been defined for the creation of data point models in the context of European supervisory reporting. Data Point Models are published by an European supervisory authority and accompanied by an XBRL taxonomy to reflect the defined data structures in a machine-readable form.
Normative references
There are currently no normative references.
Terms and definitions
There are no formal definitions that are taken from other documents.
Data Point Metamodel
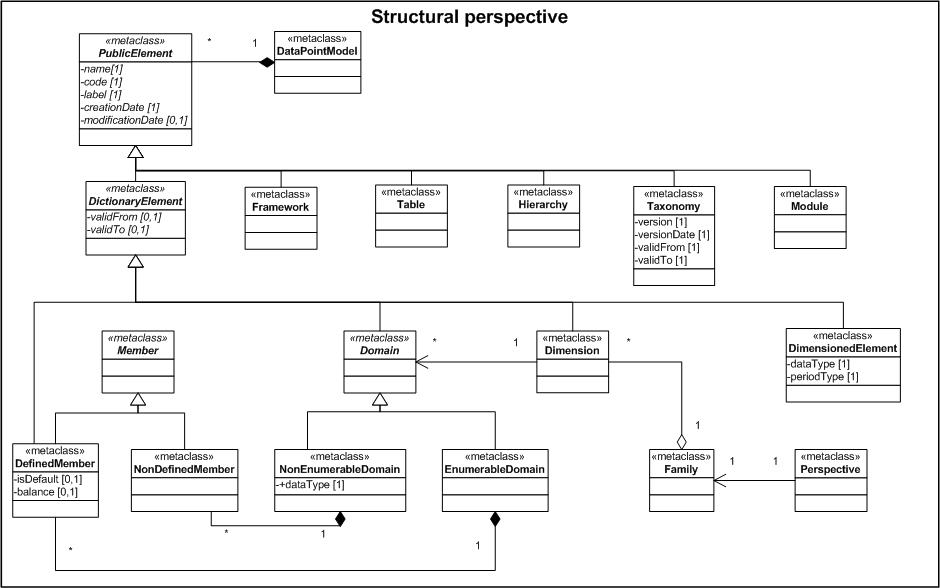
The data point meta model provides (1) the model components for the creation of a formal models on sets of data points for European supervisory reporting frameworks, (2) rules on how to combine these components and (3) the meaning (semantic) of the components and relations. Similar to a model construction kit for toys it provides the modelling principles with all characteristics available for use by the modeler. A UML class diagram is used to provide the syntax and semantic to define the metamodel for data points by showing the relevant classes and their attributes.
Classes of the Data Point Metamodel
Data Point Model
Public Element
A public element is a generalization of a concept of the model. It is identified by a code and consists of an appropriate label. Public elements have two additional attributes giving information about the date of creation and modification. Public elements are abstract and need to be specified in form of frameworks, tables, domains etc.
Dictionary Element
Framework
Table
Hierarchy
Dimension
Enumerable Dimension
Non-enumerable Dimension
Domain
Enumerable Domain
Non-enumerable Domain
Member
Defined Member
Structural Member
Dimensioned Element
Dimensioned elements represent the nature of the data with a fixed and unchangeable meaning. Dimensioned elements are strongly related to the underlying data type. Mostly they are numeric and quantatively measurable to be used for calculations and aggregations but they can be also reflect boolean or date values. A dimensioned element is the essential part of a data point that can also refer to zero or more dimensions with its according set of members.
Superclass
Dictionary Element